Active-Prompt
Chain-of-thought (CoT) methods rely on a fixed set of human-annotated exemplars. The problem with this is that the exemplars might not be the most effective examples for the different tasks. To address this, Diao et al., (2023) (opens in a new tab) recently proposed a new prompting approach called Active-Prompt to adapt LLMs to different task-specific example prompts (annotated with human-designed CoT reasoning).
Chain-of-thought(CoT)方法依賴於一組固定的人工標註範例。問題在於,這些範例可能不是不同任務最有效的範例。為瞭解決這個問題,Diao et al.,(2023) (opens in a new tab) 最近提出了一種新的提示方法,稱為Active-Prompt,以適應LLMs到不同的任務特定範例提示(用人設計的CoT推理進行標註)。
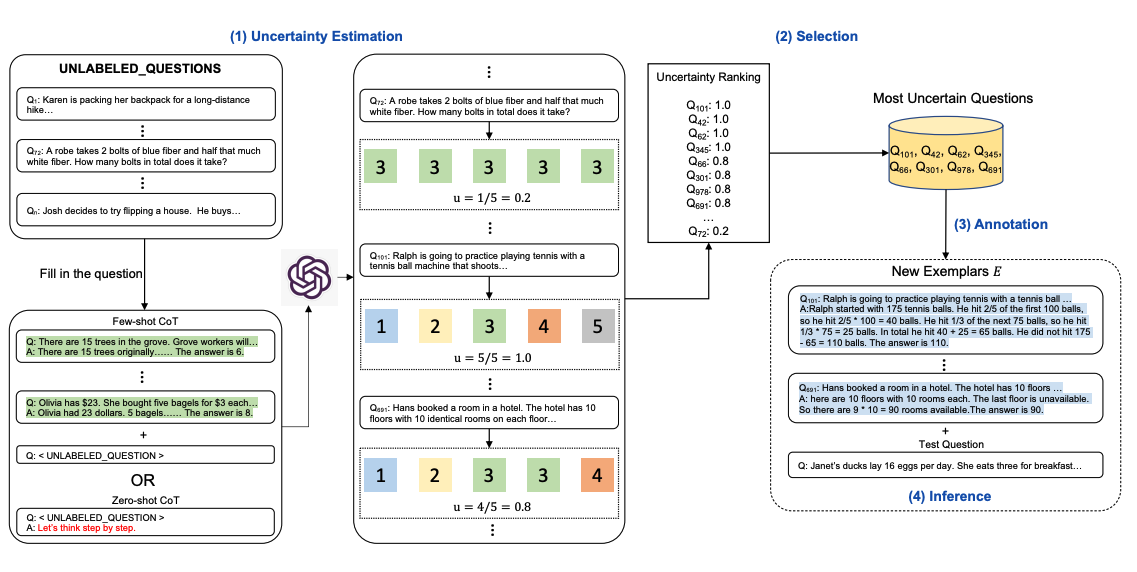
Below is an illustration of the approach. The first step is to query the LLM with or without a few CoT examples. k possible answers are generated for a set of training questions. An uncertainty metric is calculated based on the k answers (disagreement used). The most uncertain questions are selected for annotation by humans. The new annotated exemplars are then used to infer each question.
以下是方法的示意圖。第一步是使用LLM查詢帶有或不帶有一些CoT示範。對於一組訓練問題,產生k個可能的答案。基於k個答案計算不確定度度量(使用不一致性)。選擇最不確定的問題由人類進行註釋。然後使用新的註釋示範來推斷每個問題。